ATM Activiti provides JSON as a data type.
Creating/Updating/Reading JSON variables
Java Service Task
Within java service task we can create JsonNode (com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode) and set the variable.
String jsonString = "{"
+"\"id\": 1,"
+"\"name\" : {\"first\" : \"Yong\",\"last\" : \"Mook Kim\"},"
+"\"priority\" : 5"
+"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
JsonNode root = mapper.readTree(jsonString);
execution.createVariableLocal("testJsonVar", root);An Expression
Within expressions, We can query content using functionalities provided in Jackson library.
<sequenceFlow id="flow4" sourceRef="exclusivegateway1" targetRef="usertask3">
<conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression">
<![CDATA[${testJsonVar.get("priority").asInt() > 10}]]>
</conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
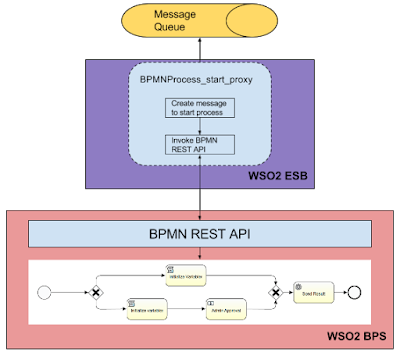
BPMN REST API
From REST API side, we cannot set JSON variable over BPMN Rest API. But possible to add that functionality by creating variable converters for JSON in REST API in WSO2 BPS v3.5.0 and v3.5.1.
Script Task
Can read JSON variables and manipulate, but cannot set JSON variables within a script in WSO2 BPS v3.5.0 and v3.5.1